Time Synchronization Protocol v2
This protocol is used to synchronize clocks on MAVLink components by estimating their time offset.
The protocol uses just one message TIMESYNC, which has two int64_t fields: tc1 and ts1. A component that wants to synchronize clocks sends out a TIMESYNC request with its current timestamp in ts1. A remote system that supports the protocol sends a TIMESYNC response, including both the original timestamp and its own timestamp. The original system can use this information to determine the round-trip time, and estimate the timestamp offset.
This sequence is run multiple times and filtered/averaged to reduce the transient effects of the channel and processor usage on the offset calculation.
INFO
This version replaces Time Synchronization Protocol v1.
Message/Enum Summary
| 消息 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| TIMESYNC | Time synchronization message. |
Sequences
The sequence is:
A component that needs time synchronization sends a
TIMESYNCrequest that includes its current nanosecond timestamp ints1(andtc1 = 0, indicating it is a request). This message may be broadcast, or targeted to a particular component.A component that receives a
TIMESYNCrequest (TIMESYNC.tc1 == 0) responds with aTIMESYNCresponse (tc1 ≠ 0) that includes the original timestamp from the request ints1(mirrored), and its own timestamp intc1.When the synchronizing component gets a
TIMESYNCresponse with its owntarget_systemandtarget_componentit knows it is a reply to a timesync request that it sent.From the message the system can:
- determine the round trip time (by comparing its current timestamp with the original stamp that was returned in the message in
ts1). - estimate the offset between system timestamps, using the round trip time and the timestamp sent back by the remote system.
INFO
TIMESYNC` responses to the broadcast address indicate that the remote system supports Time Synchronization Protocol v1. Synchronization may be unreliable if there are multiple synchronising components on the network (report/log an error and upgrade the remote system). The component should ignore responses to all other addresses.
- determine the round trip time (by comparing its current timestamp with the original stamp that was returned in the message in
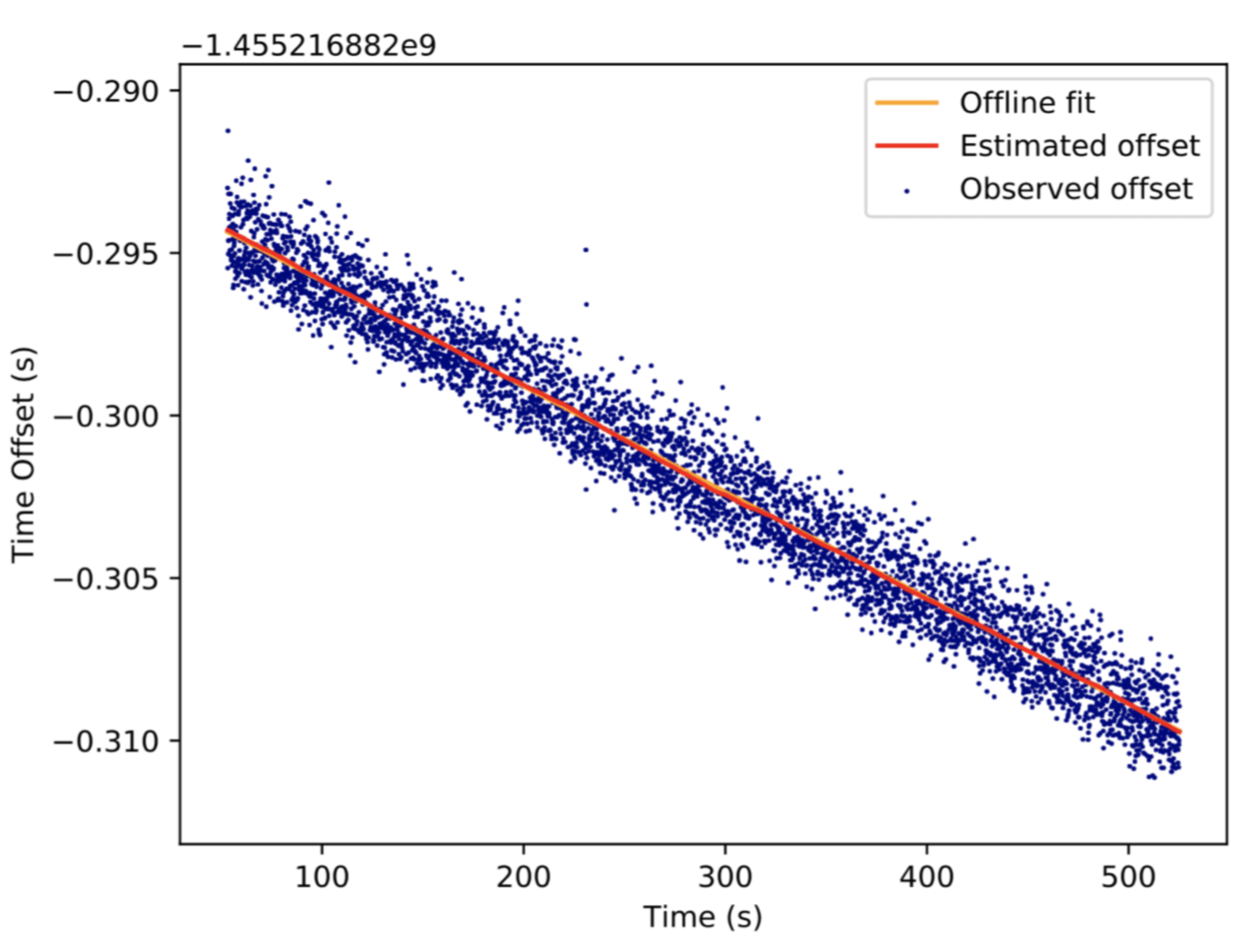
The offset is an estimate because the time spent, both inbound and outbound, will change over time based on things like link congestion and processing time. Therefore the above sequence might be run a significant number of times, and filtering used to remove outlying estimates. Therefore the above sequence might be run a significant number of times, and filtering used to remove outlying estimates.
A graph showing the "noise" when estimating the offset is given below (from PX4).
Time Synchronization Protocol v1
Version 1 of the timesync protocol uses the same message and sequences as version 2.
The difference is the TIMESYNC message in version 1 did not have target_system and target_component fields, and so the message was always broadcast. This could result in unreliable timesync if there are multiple synchronizing components on the network, because there is no way for a component to know whether a TIMESYNC response is to its request.
INFO
ArduPilot encodes the system id in TIMESYNC.ts1 of the request. This allows filtering of the response to a particular system (but not component), reducing the risk of clashes.
INFO
Version 2 adds the target address, so a syncing system can filter on just the responses to its requests.


